Workflows
This page can contain a short introduction to the workflows provided by aiida-kkr.
Density of states
The density of states (DOS) workflow kkr_dos_wc automatically sets the right parameters in the
input of a KKR calculation to perform a DOS calculation. The specifics of the DOS
energy contour are set via the wf_parameters input node which contains default values
if no user input is given.
Note
The default values of the wf_parameters input node can be extraced using
kkr_dos_wc.get_wf_defaults().
- Inputs:
kkr(aiida.orm.Code): KKRcode using thekkr.kkrpluginremote_data(RemoteData): The remote folder of the (converged) calculation whose output potential is used as input for the DOS runwf_parameters(ParameterData, optional): Some settings of the workflow behavior (e.g. number of energy points in DOS contour etc.)options(ParameterData, optional): Some settings for the computer you want to use (e.g. queue_name, use_mpi, resources, …)label(str, optional): Label of the workflowdescription(str, optional): Longer description of the workflow
- Returns nodes:
dos_data(XyData): The DOS data on the DOS energy contour (i.e. at some finite temperature)dos_data_interpol(XyData): The interpolated DOS from the line parallel to the real axis down onto the real axisresults_wf(ParameterData): The output node of the workflow containing some information on the DOS run
Note
The x and y arrays of the dos_data output nodes can easily be accessed using:
x = dos_data_node.get_x()
y = dos_data_node.get_y()
where the returned list is of the form [label, numpy-array-of-data, unit] and the
y-array contains entries for total DOS, s-, p-, d-, …, and non-spherical contributions to the DOS, e.g.:
[(u'interpolated dos tot', array([[...]]), u'states/eV'),
(u'interpolated dos s', array([[...]]), u'states/eV'),
(u'interpolated dos p', array([[...]]), u'states/eV'),
(u'interpolated dos d', array([[...]]), u'states/eV'),
(u'interpolated dos ns', array([[...]]), u'states/eV')]
Note that the output data are 2D arrays containing the atom resolved DOS, i.e. the DOS values for all atoms in the unit cell.
Example Usage
We start by getting an installation of the KKRcode:
from aiida.orm import Code
kkrcode = Code.get_from_string('KKRcode@my_mac')
Next load the remote folder node of the previous calculation (here the converged calculation of the Cu bulk test case) from which we want to start the following DOS calculation:
# import old KKR remote folder
from aiida.orm import load_node
kkr_remote_folder = load_node(22852).out.remote_folder
Then we set some settings of the workflow parameters (this step is optional):
# create workflow settings
from aiida.orm import DataFactory
ParameterData = DataFactory('parameter')
workflow_settings = ParameterData(dict={'dos_params':{'emax': 1, 'tempr': 200, 'emin': -1,
'kmesh': [20, 20, 20], 'nepts': 81}})
Finally we run the workflow:
from aiida_kkr.workflows.dos import kkr_dos_wc
from aiida.work import run
run(kkr_dos_wc, _label='test_doscal', _description='My test dos calculation.',
kkr=kkrcode, remote_data=kkr_remote_folder, wf_parameters=workflow_settings)
The following script can be used to plot the total interpolated DOS (in the
dos_data_interpol output node that can for example be access using
dos_data_interpol = <kkr_dos_wc-node>.out.dos_data_interpol where
<kkr_dos_wc-node> is the workflow node) of the calculation above:
def plot_dos(dos_data_node):
x = dos_data_node.get_x()
y_all = dos_data_node.get_y()
from matplotlib.pylab import figure, xlabel, ylabel, axhline, axvline, plot, legend, title
figure()
# loop over contributions (tot, s, p, d, ns)
for y in y_all:
if y==y_all[0]: # special line formatting for total DOS
style = 'x-'
lw = 3
else:
style = '--'
lw = 2
plot(x[1][0], y[1][0], style, lw=lw, ms=6, label=y[0].split('dos ')[1])
# add axis labels etc
xlabel(x[0]+' ({})'.format(x[-1]))
ylabel(y[0].replace(' ns','')+' ({})'.format(y[-1]))
axhline(0, color='grey', linestyle='dotted', zorder=-100)
axvline(0, color='grey', linestyle='dotted', zorder=-100)
legend(loc=2)
title('DOS of bulk Cu')
plot_dos(dos_data_interpol)
which will produce the following plot:
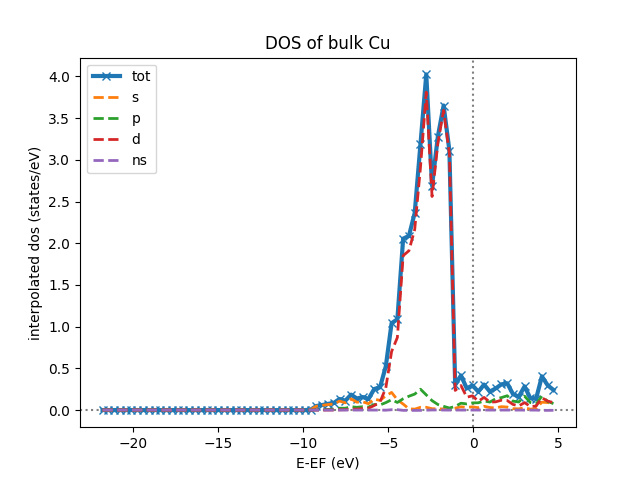
Bandstructure
The bandstructure calculation, using workchain kkr_bs_wc, yields the band structure in terms of the Bloch spectral function. To run the bandstructure calculation all the requried parameters are taken from the parent (converved) KkrCalculation and user-defined wf_parameters.
Note
Use kkr_bs_wc.get_wf_defaults() to get the default values for the wf_parameters input.
Inputs:
wf_parameters(Dict, optional): Workchain Specifications, containsnepts(int),tempr(float),emin(eV),emax(eV),rclustz(float, in units of the lattice constant). The energy range given byeminandemaxare given relative to the Fermi level.
options(Dict, optional): Computer Specifications, schedualer command, parallelization, walltime etc.
kpoints(KpointsData, optional): k-point path used in the bandstructure calculation. If it is not given it is extructed from the structure. (Although it is important the k-points should come from the primitive structure, internally it will be consider in the next version.)
remote_data(RemoteData, mendaory): Parent folder of a converged KkrCalculation.
kkr(Code, mendaory): KKRhost code (i.e. usingkkr.kkrplugin).
label(Str, optional): label for the bandstructure WorkChainNode. Can also be found in theresult_wfoutput Dict asBS_wf_labelkey.
description(Str, optional) : description for the bandstructure WorkChainNode. Can be found in theresult_wfoutput Dict asBS_wf_descriptionkey
- Returns nodes:
BS_Data(ArrayData): Consist of (BlochSpectralFunction, numpy array), (k_points, numpy array), (energy_points, numpy array), (special_kpoints, dict)result_wf(Dict): work_chain_specifications (such as ‘ successful ’, ‘ list_of_errors ’, ‘ BS_params ’ etc) node , BS_data (‘ BlochSpectralFunction ’,‘ Kpts ’,‘ energy_points ’, ‘ k-labels ’ ) node.
Access To Data:
To access into the data
BS_Data = <WC_NODE>.outputs.BS_Data
bsf = BS_Data.get_array('BlochSpectralFunction')
kpts = BS_Data.get_array('Kpts')
eng_pts = BS_Data.get_array('energy_points')
k_label= BS_Data.extras['k-labels']
The bsf array is a 2d-numpy array and contains the Bloch spectral function (k and energy resolved density) and k_label give the python dict archiving the high-symmetry points, index:label, in kpts.
Example Usage:
To start the Band Structure calculation the steps:
from aiida.orm import load_node, Str, Code, Dict
# setup the code and computer
kkrcode = Code.get_from_string('KKRcode@COMPUTERNAME')
# import the remote folder from the old converged kkr calculation
kkr_remote_folder = load_node(<KKR_CALC_JOB_NODE_ID>).outputs.remote_folder
# create workflow parameter settings
workflow_parameters = Dict(dict={'emax': 5, # in eV, relative to EF
'tempr': 50.0, # in K
'emin': -10, # in eV
'rclustz' : 2.3, # alat units
'nepts': 6})
# Computer configuration
metadata_option_1 = Dict(dict={
'max_wallclock_seconds': 36000,
'resources': {'tot_num_mpiprocs': 48, 'num_machines': 1},
'custom_scheduler_commands':
'#SBATCH --account=jara0191\n\nulimit -s unlimited; export OMP_STACKSIZE=2g',
'withmpi': True})
label = Str('testing_the_kkr_bs_wc')
inputs = {'wf_parameters':workflow_parameters,'options':metadata_option_1,'remote_data':kkr_remote_folder,'kkr':kkrcode,'label':label}
from aiida_kkr.workflows.bs import kkr_bs_wc
from aiida.engine import run
run(kkr_bs_wc, **inputs)
To plot :
To plot one or more kkr_bs_wc node.
from aiida import load_profile
load_profile()
NODE = <singel or list of nodes>
from aiida_kkr.tools import plot_kkr
plot_kkr( NODE, strucplot=False, logscale=True, silent=True, noshow=True)
For bulk Cu this results in a plot like this:
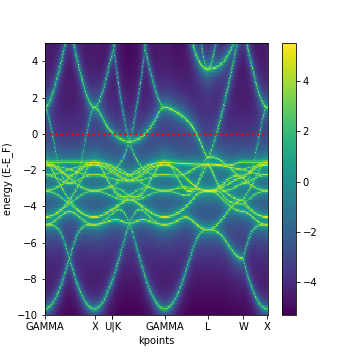
Generate KKR start potential
Workflow: kkr_startpot_wc
- Inputs:
structure(StructureData):voronoi(Code):kkr(Code):wf_parameters(ParameterData, optional):options(ParameterData, optional): Some settings for the computer you want to use (e.g. queue_name, use_mpi, resources, …)calc_parameters(ParameterData, optional):label(str, optional):description(str, optional):
Note
The default values of the wf_parameters input node can be extraced using
kkr_dos_wc.get_wf_defaults() and it should contain the following entries:
- General settings:
r_cls(float):natom_in_cls_min(int):fac_cls_increase(float):num_rerun(int):
- Computer settings:
walltime_sec(int):custom_scheduler_commands(str):use_mpi(bool):queue_name(str):resources(dict):{'num_machines': 1}
- Settings for DOS check of starting potential:
check_dos(bool):threshold_dos_zero(float):delta_e_min(float):delta_e_min_core_states(float):dos_params(dict): with the keysemax(float):tempr(float):emin(float):kmesh([int, int, int]):nepts(int):
- Output nodes:
last_doscal_dosdata(XyData):last_doscal_dosdata_interpol(XyData):last_doscal_results(ParameterData):last_params_voronoi(ParameterData):last_voronoi_remote(RemoteData):last_voronoi_results(ParameterData):results_vorostart_wc(ParameterData):
Example Usage
First load KKRcode and Voronoi codes:
from aiida.orm import Code
kkrcode = Code.get_from_string('KKRcode@my_mac')
vorocode = Code.get_from_string('voronoi@my_mac')
Then choose some settings for the KKR specific parameters (LMAX cutoff etc.):
from aiida_kkr.tools.kkr_params import kkrparams
kkr_settings = kkrparams(NSPIN=1, LMAX=2)
Now we create a structure node for the system we want to calculate:
# create Copper bulk aiida Structure
from aiida.orm import DataFactory
StructureData = DataFactory('structure')
alat = 3.61 # lattice constant in Angstroem
bravais = alat*array([[0.5, 0.5, 0], [0.5, 0, 0.5], [0, 0.5, 0.5]]) # Bravais matrix in Ang. units
Cu = StructureData(cell=bravais)
Cu.append_atom(position=[0,0,0], symbols='Cu')
Finally we run the kkr_startpot_wc workflow (here using the defaults for the workflow settings):
from aiida_kkr.workflows.voro_start import kkr_startpot_wc
from aiida.work import run
ParameterData = DataFactory('parameter')
run(kkr_startpot_wc, structure=Cu, voronoi=vorocode, kkr=kkrcode, calc_parameters=ParameterData(dict=kkr_settings.get_dict()))
KKR scf cycle
Workflow: kkr_scf_wc
Inputs:
{'strmix': 0.03, 'brymix': 0.05, 'init_pos': None, 'convergence_criterion': 1e-08,
'custom_scheduler_commands': '', 'convergence_setting_coarse': {'npol': 7, 'tempr': 1000.0,
'n1': 3, 'n2': 11, 'n3': 3,
'kmesh': [10, 10, 10]},
'mixreduce': 0.5, 'mag_init': False, 'retreive_dos_data_scf_run': False,
'dos_params': {'emax': 0.6, 'tempr': 200, 'nepts': 81, 'kmesh': [40, 40, 40], 'emin': -1},
'hfield': 0.02, 'queue_name': '', 'threshold_aggressive_mixing': 0.008,
'convergence_setting_fine': {'npol': 5, 'tempr': 600.0, 'n1': 7, 'n2': 29, 'n3': 7,
'kmesh': [30, 30, 30]},
'use_mpi': False, 'nsteps': 50, 'resources': {'num_machines': 1}, 'delta_e_min': 1.0,
'walltime_sec': 3600, 'check_dos': True, 'threshold_switch_high_accuracy': 0.001,
'kkr_runmax': 5, 'threshold_dos_zero': 0.001}
_WorkChainSpecInputs({'_label': None, '_description': None, '_store_provenance': True,
'dynamic': None, 'calc_parameters': None, 'kkr': None, 'voronoi': None,
'remote_data': None, 'wf_parameters': <ParameterData: uuid: b132dfc4-3b7c-42e7-af27-4083802aff40 (unstored)>,
'structure': None})
Outputs:
{'final_dosdata_interpol': <XyData: uuid: 0c14146d-90aa-4eb8-834d-74a706e500bb (pk: 22872)>,
'last_InputParameters': <ParameterData: uuid: 28a277ad-8998-4728-8296-75fd3b0c4eb4 (pk: 22875)>,
'last_RemoteData': <RemoteData: uuid: d24cdfc1-938a-4308-b273-e0aa8697c975 (pk: 22876)>,
'last_calc_out': <ParameterData: uuid: 1c8fab2d-e596-4874-9516-c1387bf7db7c (pk: 22874)>,
'output_kkr_scf_wc_ParameterResults': <ParameterData: uuid: 0f21ac18-e556-49f8-aa26-55260d013fac (pk: 22878)>,
'results_vorostart': <ParameterData: uuid: 93831550-8775-493a-907b-27a470b52dc8 (pk: 22877)>,
'starting_dosdata_interpol': <XyData: uuid: 54fa57ad-f559-4837-ba1e-7db4ed67d5b0 (pk: 22873)>}
Example Usage
Case 1: Start from previous calculation
from aiida.orm import Code
kkrcode = Code.get_from_string('KKRcode@my_mac')
vorocode = Code.get_from_string('voronoi@my_mac')
from aiida_kkr.tools.kkr_params import kkrparams
kkr_settings = kkrparams(NSPIN=1, LMAX=2)
from aiida.orm import load_node
kkr_startpot = load_node(22586)
last_vorono_remote = kkr_startpot.get_outputs_dict().get('last_voronoi_remote')
from aiida_kkr.workflows.kkr_scf import kkr_scf_wc
from aiida.work import run
ParameterData = DataFactory('parameter')
run(kkr_scf_wc, kkr=kkrcode, calc_parameters=ParameterData(dict=kkr_settings.get_dict()), remote_data=last_vorono_remote)
Case 2: Start from structure and run voronoi calculation first
# create Copper bulk aiida Structure
fro numpy import array
from aiida.orm import DataFactory
StructureData = DataFactory('structure')
alat = 3.61 # lattice constant in Angstroem
bravais = alat*array([[0.5, 0.5, 0], [0.5, 0, 0.5], [0, 0.5, 0.5]]) # Bravais matrix in Ang. units
Cu = StructureData(cell=bravais)
Cu.append_atom(position=[0,0,0], symbols='Cu')
run(kkr_scf_wc, structure=Cu, kkr=kkrcode, voronoi=vorocode, calc_parameters=ParameterData(dict=kkr_settings.get_dict()))
KKR flex (GF calculation)
The Green’s function writeout workflow performs a KKR calculation with runoption
KKRFLEX to write out the kkr_flexfiles. Those are needed for a kkrimp
calculation.
- Inputs:
kkr(aiida.orm.Code): KKRcode using thekkr.kkrpluginremote_data(RemoteData): The remote folder of the (converged) kkr calculationimp_info(ParameterData): ParameterData node containing the information of the desired impurities (needed to write out thekkr_flexfilesand thescoeffile)options(ParameterData, optional): Some settings for the computer (e.g. computer settings)wf_parameters(ParameterData, optional): Some settings for the workflow behaviourlabel(str, optional): Label of the workflowdescription(str, optional): Longer description of the workflow
- Returns nodes:
workflow_info(ParameterData): Node containing general information about the workflow (e.g. errors, computer information, …)GF_host_remote(RemoteData): RemoteFolder with all of thekkrflexfilesand further output of the workflow
Example Usage
We start by getting an installation of the KKRcode:
from aiida.orm import Code
kkrcode = Code.get_from_string('KKRcode@my_mac')
Next load the remote folder node of the previous calculation (here the converged calculation of the Cu bulk test case) from which we want to start the following KKRFLEX calculation:
# import old KKR remote folder
from aiida.orm import load_node
kkr_remote_folder = load_node(<pid of converged calc>).out.remote_folder
Afterwards, the information regarding the impurity has to be given
(in this example, we use a Au impurity with a cutoff radius of 2 alat which is placed in the first labelled lattice point of the unit cell). Further keywords for the impurity_info node can be found in the respective part of the documentation:
# set up impurity info node
imps = ParameterData(dict={'ilayer_center':0, 'Rcut':2, 'Zimp':[79.]})
Then we set some settings of the options parameters (this step is optional):
# create workflow settings
from aiida.orm import DataFactory
ParameterData = DataFactory('parameter')
options = ParameterData(dict={'use_mpi':'false', 'queue_name':'viti_node', 'walltime_sec' : 60*60*2,
'resources':{'num_machines':1, 'num_mpiprocs_per_machine':1}})
Finally we run the workflow:
from aiida_kkr.workflows.gf_writeout import kkr_flex_wc
from aiida.work import run
run(kkr_flex_wc, label='test_gf_writeout', description='My test KKRflex calculation.',
kkr=kkrcode, remote_data=kkr_remote_folder, options=options, wf_parameters=wf_params)
Exchange coupling constants
Calculation of the exchange coupling constants (Jij’s and Dij’s) can be done with the kkr_jij_wc workchain starting from the remote folder of a parent calculation.
Note
Use kkr_jij_wc.get_wf_defaults() to get the default values for the wf_parameters input.
Inputs:
wf_parameters(Dict, optional): Workchain settings where the Jij radius in Angstroem units is given (defaults to 5 Ang.). Withjijsite_iandjijsite_jone can specify to calculate the Jij’s only for some pairs i,j.
options(Dict, optional): Computer options (scheduler command, parallelization, walltime etc.)
remote_data(RemoteData, mandatory): Parent folder of a converged KkrCalculation.
kkr(Code, mandatory): KKRhost code (i.e. usingkkr.kkrplugin).
params_kkr_overwrite(Dict, optional): Optional set of KKR parameters that overwrite the settings extracted from the parent calculation.
- Returns nodes:
jij_data(ArrayData): Jij data with the arraysJij_expandedthat contains all (i, j, da, db, dc, Jij [, Dij]) pairs andpositions_expandedthat contains the corresponding positions (i.e. the offset of j vs i).structure_jij_sites(StructureData): Structure with the Jij sites that match the mapping injij_data
To start the Band Structure calculation the steps:
from aiida_kkr.workflows import kkr_jij_wc
# converged KKR calculation
kkr_calc_converged = load_node(<PK>)
# create process builder
builder = kkr_jij_wc.get_builder()
builder.parent_folder = kkr_calc_converged.outputs.remote_folder
builder.kkr = parent.inputs.code
builder.options = Dict(dict={...}) # settings for the computer that we use
wfd = kkr_jij_wc.get_wf_defaults()
wfd['jijrad_ang'] = 5.0 # set at least the Jij cutoff radius in Ang units
builder.wf_parameters = Dict(dict=wfd)
# maybe overwrite some input parameters
# here we switch on the SOC mode starting from a no SOC calculation
builder.params_kkr_overwrite = Dict(dict={
'NPAN_LOG': 5,
'NPAN_EQ': 15,
'NCHEB': 12,
'R_LOG': 0.6,
'USE_CHEBYCHEV_SOLVER': True,
'SET_CHEBY_NOSOC': True
})
# submit calculation
jij_wf = submit(builder)
KKR impurity self consistency
This workflow performs a KKRimp self consistency calculation starting from a given host-impurity startpotential and converges it.
Note
This workflow does only work for a non-magnetic calculation without spin-orbit-coupling. Those two features will be added at a later stage. This is also just a sub workflow, meaning that it only converges an already given host-impurity potential. The whole kkrimp workflow starting from scratch will also be added at a later stage.
- Inputs:
kkrimp(aiida.orm.Code): KKRimpcode using thekkr.kkrimppluginhost_imp_startpot(SinglefileData, optional): File containing the host impurity potential (potential file with the whole cluster with all host and impurity potentials)remote_data(RemoteData, optional): Output from a KKRflex calculation (can be extracted from the output of the GF writeout workflow)kkrimp_remote(RemoteData, optional): RemoteData output from previous kkrimp calculation (if given,host_imp_startpotis not needed as input)impurity_info(ParameterData, optional): Node containing information about the impurity cluster (has to be chosen consistently withimp_infofrom GF writeout step)options(ParameterData, optional): Some general settings for the workflow (e.g. computer settings, queue, …)wf_parameters(ParameterData, optional) : Settings for the behavior of the workflow (e.g. convergence settings, physical properties, …)label(str, optional): Label of the workflowdescription(str, optional): Longer description of the workflow
- Returns nodes:
workflow_info(ParameterData): Node containing general information about the workflow (e.g. errors, computer information, …)host_imp_pot(SinglefileData): Converged host impurity potential that can be used for further calculations (DOS calc, new input for different KKRimp calculation)
Example Usage
We start by getting an installation of the KKRimpcode:
from aiida.orm import Code
kkrimpcode = Code.get_from_string('KKRimpcode@my_mac')
Next, either load the remote folder node of the previous calculation (here the KKRflex calculation that writes out the GF and KKRflexfiles) or the output node of the gf_writeout workflow from which we want to start the following KKRimp calculation:
# import old KKRFLEX remote folder
from aiida.orm import load_node
GF_host_output_folder = load_node(<pid of KKRFLEX calc>).out.remote_folder # 1st possibility
# GF_host_output_folder = load_node(<pid of gf_writeout wf output node>) # 2nd possibility: take ``GF_host_remote`` output node from gf_writeout workflow
Now, load a converged calculation of the host system (here Cu bulk) as well as an auxiliary voronoi calculation (here Au) for the desired impurity:
# load converged KKRcalc
kkrcalc_converged = load_node(<pid of converged KKRcalc (Cu bulk)>)
# load auxiliary voronoi calculation
voro_calc_aux = load_node(<pid of voronoi calculation for the impurity (Au)>)
Using those, one can obtain the needed host-impurity potential that is needed as input for the workflow. Therefore,
we use the neworder_potential_wf workfunction which is able to generate the startpot:
## load the neccessary function
from aiida_kkr.tools.common_workfunctions import neworder_potential_wf
import numpy as np
# extract the name of the converged host potential
potname_converged = kkrcalc_converged._POTENTIAL
# set the name for the potential of the desired impurity (here Au)
potname_imp = 'potential_imp'
neworder_pot1 = [int(i) for i in np.loadtxt(GF_host_calc.out.retrieved.get_abs_path('scoef'), skiprows=1)[:,3]-1]
potname_impvorostart = voro_calc_aux._OUT_POTENTIAL_voronoi
replacelist_pot2 = [[0,0]]
# set up settings node to use as argument for the neworder_potential function
settings_dict = {'pot1': potname_converged, 'out_pot': potname_imp, 'neworder': neworder_pot1,
'pot2': potname_impvorostart, 'replace_newpos': replacelist_pot2, 'label': 'startpot_KKRimp',
'description': 'starting potential for Au impurity in bulk Cu'}
settings = ParameterData(dict=settings_dict)
# finally create the host-impurity potential (here ``startpot_Au_imp_sfd``) using the settings node as well as
the previously loaded converged KKR calculation and auxiliary voronoi calculation:
startpot_Au_imp_sfd = neworder_potential_wf(settings_node=settings,
parent_calc_folder=kkrcalc_converged.out.remote_folder,
parent_calc_folder2=voro_calc_aux.out.remote_folder)
Note
Further information how the neworder potential function works can be found in the respective part of this documentation.
Afterwards, the information regarding the impurity has to be given
(in this example, we use a Au impurity with a cutoff radius of 2 alat which is placed in the first labelled lattice point of the unit cell). Further
keywords for the impurity_info node can be found in the respective part of the documentation:
# set up impurity info node
imps = ParameterData(dict={'ilayer_center':0, 'Rcut':2, 'Zimp':[79.]})
Then, we set some settings of the options parameters on the one hand and specific wf_parameters regarding the convergence etc.:
options = ParameterData(dict={'use_mpi':'false', 'queue_name':'viti_node', 'walltime_sec' : 60*60*2,
'resources':{'num_machines':1, 'num_mpiprocs_per_machine':20}})
kkrimp_params = ParameterData(dict={'nsteps': 50, 'convergence_criterion': 1*10**-8, 'strmix': 0.1,
'threshold_aggressive_mixing': 3*10**-2, 'aggressive_mix': 3,
'aggrmix': 0.1, 'kkr_runmax': 5})
Finally we run the workflow:
from aiida_kkr.workflows.kkr_imp_sub import kkr_imp_sub_wc
from aiida.work import run
run(kkr_imp_sub_wc, label='kkr_imp_sub test (CuAu)', description='test of the kkr_imp_sub workflow for Cu, Au system',
kkrimp=kkrimpcode, options=options, host_imp_startpot=startpot_Au_imp_sfd,
remote_data=GF_host_output_folder, wf_parameters=kkrimp_params)
KKR impurity workflow
This workflow performs a KKR impurity calculation starting from an impurity_info node
as well as either from a coverged calculation remote for the host system (1) or from a
GF writeout remote (2). In the two cases the following is done:
(1): First, the host system will be converged using the
kkr_scfworkflow. Then, the GF will be calculated using thegf_writeoutworkflow before calculating the auxiliary startpotential of the impurity. Now, the total impurity-host startpotential will be generated and then converged using thekkr_imp_subworkflow.(2): In this case the two first steps from above will be skipped and the workflow starts by calculating the auxiliary startpotential.
Note
This workflow is different from the kkr_imp_sub workflow that only converges a given
impurity host potential. Here, the whole process of a KKR impurity calculation is done
automatically.
- Inputs:
kkrimp(aiida.orm.Code): KKRimpcode using thekkr.kkrimppluginvoronoi(aiida.orm.Code): Voronoi code using thekkr.voropluginkkr(aiida.orm.Code): KKRhost code using thekkr.kkrpluginimpurity_info(ParameterData): Node containing information about the impurity clusterremote_data_host(RemoteData, optional): RemoteData of a converged host calculation if you want to start the workflow from scratchremote_data_gf(RemoteData, optional): RemoteData of a GF writeout step (if you want to skip the convergence of the host and the GF writeout step)options(ParameterData, optional): Some general settings for the workflow (e.g. computer settings, queue, …)wf_parameters(ParameterData, optional) : Settings for the behavior of the workflow (e.g. convergence settings, physical properties, …)voro_aux_parameters(ParameterData, optional): Settings for the usage of thekkr_startpotsub workflow needed for the auxiliary voronoi potentialslabel(str, optional): Label of the workflowdescription(str, optional): Longer description of the workflow
- Returns nodes:
workflow_info(ParameterData): Node containing general information about the workflowlast_calc_info(ParameterData): Node containing information about the last used calculation of the workflowlast_calc_output_parameters(ParameterData): Node with all of the output parameters from the last calculation of the workflow
Example Usage
We start by getting an installation of the codes:
from aiida.orm import Code
kkrimpcode = Code.get_from_string('KKRimpcode@my_mac')
kkrcode = Code.get_from_string('KKRcode@my_mac')
vorocode = Code.get_from_string('vorocode@my_mac')
Then, set up an appropriate impurity_info node for your calculation:
# set up impurity info node
imps = ParameterData(dict={'ilayer_center':0, 'Rcut':2, 'Zimp':[79.]})
Next, load either a gf_writeout_remote or a converged_host_remote:
from aiida.orm import load_node
gf_writeout_remote = load_node(<pid or uuid>)
converged_host_remote = load_node(<pid or uuid>)
Set up some more input parameter nodes for your workflow:
# node for general workflow options
options = ParameterData(dict={'use_mpi': False, 'walltime_sec' : 60*60*2,
'resources':{'num_machines':1, 'num_mpiprocs_per_machine':1}})
# node for convergence behaviour of the workflow
kkrimp_params = ParameterData(dict={'nsteps': 99, 'convergence_criterion': 1*10**-8, 'strmix': 0.02,
'threshold_aggressive_mixing': 8*10**-2, 'aggressive_mix': 3,
'aggrmix': 0.04, 'kkr_runmax': 5, 'calc_orbmom': False, 'spinorbit': False,
'newsol': False, 'mag_init': False, 'hfield': [0.05, 10],
'non_spherical': 1, 'nspin': 2})
# node for parameters needed for the auxiliary voronoi workflow
voro_aux_params = ParameterData(dict={'num_rerun' : 4, 'fac_cls_increase' : 1.5, 'check_dos': False,
'lmax': 3, 'gmax': 65., 'rmax': 7., 'rclustz': 2.})
Finally, we run the workflow (for the two cases depicted above):
from aiida_kkr.workflows.kkr_scf import kkr_scf_wc
from aiida_kkr.workflows.voro_start import kkr_startpot_wc
from aiida_kkr.workflows.kkr_imp_sub import kkr_imp_sub_wc
from aiida_kkr.workflows.gf_writeout import kkr_flex_wc
from aiida_kkr.workflows.kkr_imp import kkr_imp_wc
from aiida.work.launch import run, submit
# don't forget to set a label and description for your workflow
# case (1)
wf_run = submit(kkr_imp_wc, label=label, description=description, voronoi=vorocode, kkrimp=kkrimpcode,
kkr=kkrcode, options=options, impurity_info=imps, wf_parameters=kkrimp_params,
voro_aux_parameters=voro_aux_params, remote_data_gf=gf_writeout_remote)
# case (2)
wf_run = submit(kkr_imp_wc, label=label, description=description, voronoi=vorocode, kkrimp=kkrimpcode,
kkr=kkrcode, options=options, impurity_info=imps, wf_parameters=kkrimp_params,
voro_aux_parameters=voro_aux_params, remote_data_host=converged_host_remote)
KKR impurity density of states
This workflow calculates the density of states for a given host impurity input potential.
- Inputs:
kkrimp(aiida.orm.Code): KKRimpcode using thekkr.kkrimppluginkkr(aiida.orm.Code): KKRhost code using thekkr.kkrpluginhost_imp_pot(SinglefileData): converged host impurity potential from impurity workflowoptions(ParameterData, optional): Some general settings for the workflow (e.g. computer settings, queue, …)wf_parameters(ParameterData, optional) : Settings for the behavior of the workflow (e.g. convergence settings, physical properties, …)label(str, optional): Label of the workflowdescription(str, optional): Longer description of the workflow
- Returns nodes:
workflow_info(ParameterData): Node containing general information about the workflowlast_calc_info(ParameterData): Node containing information about the last used calculation of the workflowlast_calc_output_parameters(ParameterData): Node with all of the output parameters from the last calculation of the workflow
Example Usage
We start by getting an installation of the codes:
from aiida.orm import Code
kkrimpcode = Code.get_from_string('KKRimpcode@my_mac')
vorocode = Code.get_from_string('vorocode@my_mac')
Next, load the converged host impurity potential:
from aiida.orm import load_node
startpot = load_node(<pid or uuid of SinglefileData>)
Set up some more input parameter nodes for your workflow:
# node for general workflow options
options = ParameterData(dict={'use_mpi': False, 'walltime_sec' : 60*60*2,
'resources':{'num_machines':1, 'num_mpiprocs_per_machine':1}})
# node for convergence behaviour of the workflow
wf_params = ParameterData(dict={'ef_shift': 0. ,
'dos_params': {'nepts': 61,
'tempr': 200,
'emin': -1,
'emax': 1,
'kmesh': [30, 30, 30]},
'non_spherical': 1,
'born_iter': 2,
'init_pos' : None,
'newsol' : False})
Finally, we run the workflow (for the two cases depicted above):
from aiida_kkr.workflows.kkr_imp_dos import kkr_imp_dos_wc
from aiida.work.launch import run, submit
# don't forget to set a label and description for your workflow
wf_run = submit(kkr_imp_dos_wc, label=label, description=description, kkrimp=kkrimpcode,
kkrcode=kkrcode, options=options, wf_parameters=wf_params)
Equation of states
Workflow: aiida_kkr.workflows.eos
Warning
Not documented yet!
Check KKR parameter convergence
Workflow: aiida_kkr.workflows.check_para_convergence
Warning
Not implemented yet!
- Idea is to run checks after convergence for the following parameters:
RMAX
GMAX
cluster radius
energy contour
kmesh
Find magnetic ground state
Workflow: aiida_kkr.workflows.check_magnetic_state
Warning
Not implemented yet!
The idea is to run a Jij calculation to estimate if the ferromagnetic state is the ground state or not. Then the unit cell could be doubled to compute the antiferromagnetic state. In case of noncollinear magnetism the full Jij tensor should be analyzed.